# Bragg grating sections
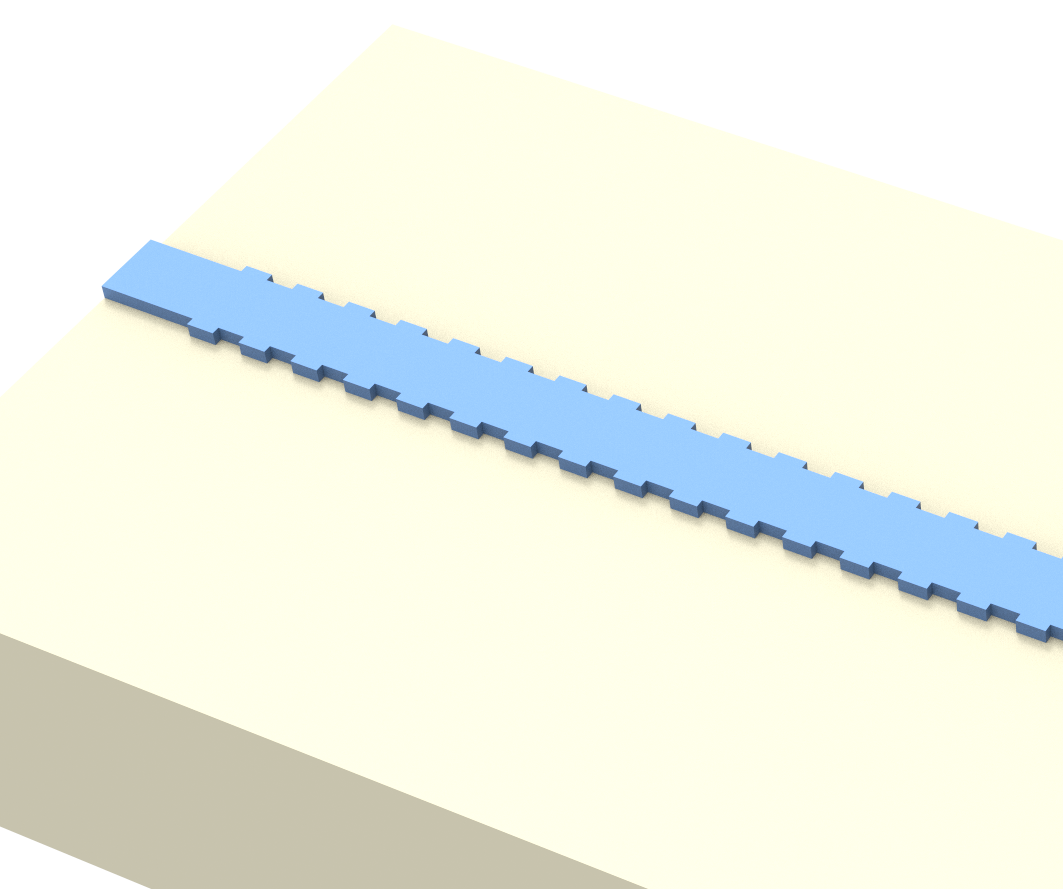
Bragg gratings are often used in waveguides, such as optical fibres, which can reflect light of certain frequencies while transmitting others. This is typically achieved by periodically changing the refractive index or dielectric constant in a section of the waveguide, and the reflective and transmitting frequency bands are controlled by appropriately designing the periodicity and material or geometry parameters of the grating.
In this example, sections of two Bragg gratings will be simulated. The first one involves a waveguide with a perfectly-aligned corrugation on either side, which causes it to act as a reflector. The second one is similar, but with the corrugation on one side misaligned with the corrugation on the other side, so that the structure primarily transmits power. The design is adapted from Xu Wang, Yun Wang, Jonas Flueckiger, Richard Bojko, Amy Liu, Adam Reid, James Pond, Nicolas A. F. Jaeger, and Lukas Chrostowski, “Precise control of the coupling coefficient through destructive interference in silicon waveguide Bragg gratings,” Opt. Lett. 39, 5519-5522 (2014) (opens new window).
To view the full example in Python, please click here (opens new window).