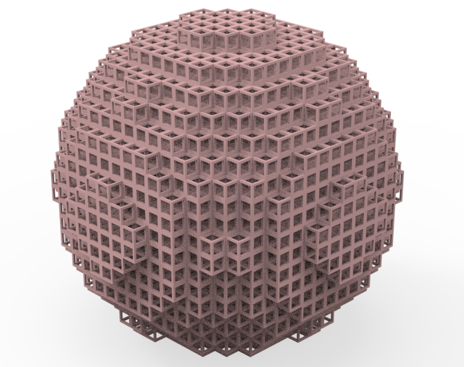
# 3D optical Luneburg lens
Luneburg lens is a prototypical gradient index (GRIN) optical component. A classical Luneburg lens is a spherical lens with a spatially varying refractive index profile following
However, it is practically difficult to construct such a lens due to the required gradient index distribution. In the microwave regime, high-gain antennas based on a Luneburg lens design can be achieved by, for example, using concentric ceremics shells with different densities. In the optical frequencies, such an approach is generally not applicable.
In this notebook, we demonstrate the numerical simulation of a practical 3D optical Luneburg lens. The structure consists of a large number of subwavelength unit cells. Using an effective medium approach, each unit cell can be approximated by a local effective index, which can be tuned by the filling fraction of the dielectric polymer in the unit cell. By varying the filling fraction of each unit cell such that the local effective index follows
To view the full example in Python, please click here (opens new window).